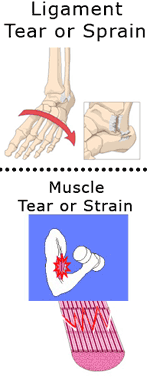
 Sprains and Strains:
Sprains and Strains:
Sprains and strains are common injuries that we sustain with daily activities, recreation, and competitive sports. But what is a sprain and what is a strain?
Strains
A strain is the tearing of muscle fibers. Muscle fibers are the individual units that make up your muscles. When you call upon the muscle to perform strong or repeated contractions, you may suffer a strain. To further confuse the layperson, strains are classified into grades I, II, and III. Another way to think of these grades is mild (grade I), moderate (grade II), severe (grade III).
- A grade I strain is a mild disruption of the muscle fibers. There may be mild swelling, mild tenderness, and it may be painful to stretch and use the injured muscle.
- A grade II muscle strain indicates moderate muscle fiber damage. The pain is moderate to severe, it definitely hurts to use and stretch the injured muscle, and ecchymosis may be present. Ecchymosis (commonly called bruising) indicates that there was internal damage to blood vessels that resulted in bleeding within and around the muscle. This bleeding is often visible under the skin as a purple, blue, red, yellow, and even green in color.
- A grade III strain is the most severe. It is the complete tearing of a muscle into two pieces, or separation of the muscle from its associated tendon. There is severe pain, complete loss of muscle strength, swelling is normally present with ecchymosis, and there may be a palpable "indentation" where the muscle is torn. Medical intervention is usually necessary. Typically, an orthopaedist (musculoskeletal specialist) will evaluate your condition and surgical repair may be necessary.
Sprains
Sprains are tears of the ligaments and capsules (tissues around joints). Ligaments are made up of bundles of somewhat elastic, collagen tissue and attach one bone to another. Capsules typically partially or completely surround a joint. In a synovial joint, there is lubricating and nourishing fluid within the capsule called synovial fluid.
Like strains, sprains are classified as grade I, II, or III in their severity.
- A grade I sprain involves a minimal number of ligament fibers. There may be pain, swelling, and only mild loss of function.
- A grade II sprain is a moderate or partial ligament tear. There is usually moderate to severe pain, swelling and bruising are typically present, and there is a loss of joint function (e.g., it is extremely difficult or you are unable to walk on a grade II ligament sprain of the ankle).
- A grade III sprain is a complete tearing of the ligament or joint capsule into two pieces. Severe pain, swelling, bruising, and loss of function are associated with a grade III sprain. As with grade III strains, orthopaedic intervention/surgical repair may be necessary.
What are my treatment options?
- Drugs
- Corticosteroid Injections
- Surgery
- Physical Therapy*
Physical Therapy for Muscle Strains and Ligament Sprains
The good news is that many sprains and strains can be treated conservatively. Our physical therapists (PTs) are experts in the art and science of the evaluation and treatment of shoulder dysfunctions (abnormalities). We care for people of all ages and successfully treat a variety of muscle, ligament, tendon, joint and neurological conditions.
Components of your care typically include:
- A thorough biomechanical evaluation.
- Customized treatment plan.
- Extensive patient education.
- Hands-on techniques to relax the muscles and recover mobility.
- Stretching for tight muscles.
- Strengthening of weak muscles.
- Mobilization of stiff joints.
- Modalities such as ice, heat, ultrasound or electrical stimulation.
Advantages of Physical Therapy:
- No side effects.
- Cost-effective.
- Supported by clinical research*.
- Customized to treat the underlying cause.
Visit our Medical Library for more information on muscle strains and ligament sprains.
